The fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) industry is undergoing a transformation as smart packaging technologies gain popularity. Smart packaging technologies have increasingly shown their effectiveness in increasing the shelf life of FMCG products. Moving beyond the traditional functions of packaging, Smart packaging integrated advanced technology, sensors, and connectivity to enhance the freshness, quality, and safety of packaged goods, thereby increasing the shelf life of these products.
Smart packaging employs two foundational pillars: active packaging and intelligent packaging. Active packaging is when technologically advanced materials that release or absorb substances are used as packaging materials to extend the shelf life of a product by slowing spoilage and microbial growth. Examples of active packaging materials include oxygen scavengers, ethylene absorbers, and antimicrobials. Intelligent packaging incorporates sensors, time-temperature indicators, biosensors, RFID/NFC chips, and QR codes into the packaging. This type of packaging provides real-time monitoring of factors like freshness, temperature, and humidity and communicates changes to consumers or other stakeholders.
Modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) that can alter gas composition inside the package to inhibit spoilage organisms or packaging using nanomaterials and bio-nanocomposites to enhance barrier properties and deliver real-time safety/quality monitoring can also be considered as part of smart packaging.
Benefits of Smart packaging in FMCG products
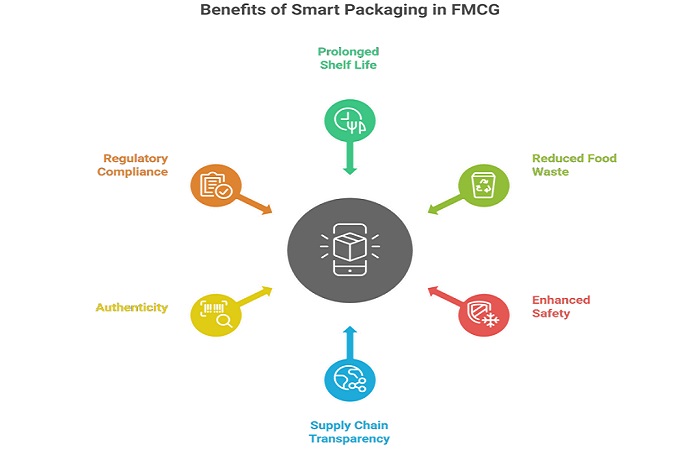
Smart packaging has various key benefits when it comes to FMCG packaging.
Prolonged Shelf Life: Smart packaging can significantly delay spoilage, oxidation, and microbial growth by controlling the microenvironment. This enables the product to stay fresh for longer periods.
Reducing Food Waste: This kind of packaging can monitor the packaged food in real time and also maintain optimal freshness—this can cut down on premature disposal, reducing food wastage and supporting sustainability goals
Enhancing Product Safety and Quality: Sensors employed by smart packaging technologies can alert to temperature change, tampering, or contamination, safeguarding consumers and brand reputation.
Improving Supply Chain Transparency: Smart packaging that uses RFID and blockchain technology allows stakeholders to track logistics, provenance, and product history from manufacturer to shelf.
Enabling Authenticity and Anti-Counterfeiting: Smart tags and digital identifiers confirm product authenticity and hence help in tackling counterfeit products in FMCG.
Facilitating Regulatory Compliance: Automated tracking and clear labelling enabled by smart packaging streamline adherence to safety and labelling requirements.
Bridging Consumer Experience and Sustainable Innovation
The FMCG industry has witnessed various applications of smart packaging techniques, with new innovations continuing to evolve. Using QR codes, NFC tags, and augmented reality in packaging offers a Interactive consumer experience, where the consumers can access real-time information on products like recipe information, etc., and access loyalty rewards—this offers brand differentiation to the advantage of the producers. For manufacturers, integrating IoT and digital twins in packaging allows seamless information flow where the packaging data is connected directly into inventory systems, logistics platforms, and consumer apps.
Greater consumer awareness of environmental and sustainability concerns has led to greater demand for sustainable products, where sustainable packaging becomes crucial. New bio-based compostable smart films and labels, which combine environmental responsibility with the active functions needed for preserving product freshness and safety is a step in this direction. As regulations get tighter, packaging companies are rapidly adopting innovative and smart packaging technologies.
Advances in Material Science Driving Smart Packaging Innovation
Innovations in materials are creating smarter, more adaptable packaging solutions that meet the growing demands of the FMCG market. The use of renewable, bio-derived polymers that provide effective barriers while being environmentally friendly is one such innovation. These bio-based and biodegradable materials can incorporate smart additives like natural antimicrobials or freshness indicators, aligning shelf-life extension with sustainability goals. Stimuli-responsive materials are available. These materials in the form of packaging films and coatings can change properties in response to environmental triggers such as temperature, humidity, or pH. For example, colour-changing indicators that visually signal freshness or spoilage without electronic components.
Nano-engineered barriers like nano-coatings and nanocomposites significantly enhance imperviousness to oxygen, moisture, and UV light, protecting sensitive FMCG products from degradation. These ultra-thin layers maintain product quality while reducing overall material usage. Materials engineered to self-repair minor damages are also available as a smart packaging choice. Anti-fogging surfaces are available, which can prevent condensation. They can prolong shelf life visually and functionally, maintaining packaging integrity and consumer appeal.
These material advances reduce reliance on bulky or toxic additives and move smart packaging towards seamless, multifunctional solutions that are user-friendly, cost-effective, and environmentally conscious. More and more FMCG companies are investing in such technologies that set new standards for freshness, convenience, and brand differentiation.
Looking forward
As the market evolves, smart packaging will become more intelligent, personalised, and integrated across the FMCG value chain. Artificial intelligence and machine learning can analyse sensor data patterns to predict spoilage or optimise packaging design dynamically. Smart packaging can also tailor content and functionality to individual consumers, dietary needs, or regional preferences using connected digital platforms. This enables personalisation at scale within the packaging sector.
Smart packaging also moots the journey towards a circular economy since employing the smart techniques helps to cut down resource wastage and enables informed decision-making for sustainability. Close collaboration with recycling industries and legislation will promote packaging designed for full lifecycle recovery or biodegradation.
Way forward, companies must invest in research and partnerships focused on sustainable smart materials and scalable technology.
Conclusion
Smart packaging is no longer a futuristic concept but an evolving reality that is drastically transforming the FMCG industry. By integrating advanced materials, sensors, and digital connectivity, smart packaging goes beyond the traditional function of containing product; rather, it actively contributes to product integrity, supply chain transparency, and consumer trust. The smart packaging industry is using technologies like oxygen-scavenging films, freshness-indicating labels, and IoT-enabled traceability to cut down on waste, extend shelf life, and satisfy the increasing need for genuine and sustainable products.
The ability to merge intelligence with environmental responsibility will define the next era of packaging, as regulatory pressure mounts and consumer expectations grow more complex. For FMCG companies, this means aligning R&D, operations, and digital transformation efforts to develop a compliant, scalable, and circular smart packaging system.





























