The Future of Paper Packaging in a Circular Economy
The packaging industry stands at a transformative crossroads where traditional linear models of “take-make-dispose” are giving way to regenerative circular systems that prioritize resource conservation and waste elimination. At the heart of this revolution lies paper packaging, a material uniquely positioned to drive the transition toward sustainable commerce through its inherent recyclability, biodegradability, and renewable sourcing capabilities.
Redefining Packaging Through Circular Principles
The circular economy paper packaging revolution represents more than just material substitution—it embodies a fundamental shift in how we conceptualize product protection, brand communication, and environmental stewardship. Unlike traditional packaging systems that end at disposal, circular economy paper packaging is designed from inception to remain in productive use through multiple lifecycles, whether through reuse, recycling, or controlled biodegradation.
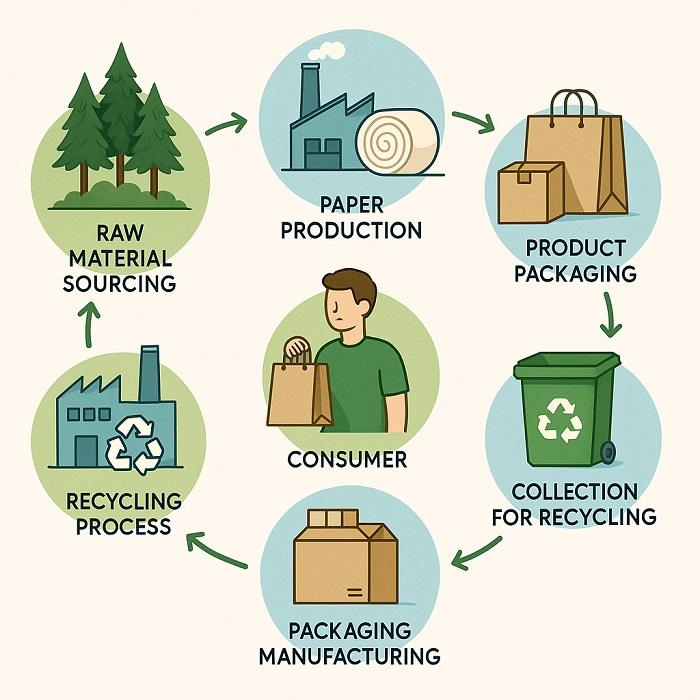
This approach aligns with the three core principles of circular design: eliminating waste and pollution, circulating products and materials at their highest value, and regenerating natural systems. Paper packaging excels across all these dimensions, offering manufacturers and consumers a pathway to reduce environmental impact while maintaining functionality and aesthetic appeal.
The Science Behind Sustainable Paper Solutions
Modern paper packaging leverages advanced manufacturing processes that maximize resource efficiency while enhancing performance characteristics. The kraft process, originally developed in the 1880s, has evolved to incorporate sustainable forestry practices, closed-loop water systems, and energy recovery technologies that minimize environmental footprint.
Contemporary paper mills increasingly utilize recycled fiber content, with some facilities achieving recycling rates exceeding 87 percent for paper-based packaging materials. This remarkable circularity coefficient demonstrates paper’s superior performance compared to alternative materials, particularly plastic packaging which achieves only 42 percent recycling rates across European markets.
Advanced coating technologies and barrier solutions now enable paper packaging to compete effectively with traditional plastic alternatives across moisture-sensitive applications. Water-resistant coatings derived from renewable sources provide protection without compromising recyclability, while innovative structural designs enhance strength and durability through engineering rather than additional material usage.
Market Dynamics Driving Circular Adoption
The global transition toward circular economy paper packaging is accelerating under multiple market pressures. Regulatory frameworks, including the European Union’s Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation and similar legislation across major markets, are establishing mandatory recyclability targets and single-use plastic restrictions that favor paper-based solutions.
Consumer preferences increasingly influence purchasing decisions, with surveys indicating that 62 percent of European consumers prefer products delivered in paper packaging for online purchases. This demand translates directly into competitive advantage for brands adopting sustainable packaging strategies, with over half of consumers actively seeking retailers committed to plastic-free packaging alternatives.

Economic incentives further reinforce circular adoption patterns. Paper packaging systems offer cost advantages through reduced raw material requirements, simplified recycling infrastructure compatibility, and decreased waste management expenses. These financial benefits become particularly pronounced as carbon pricing mechanisms and extended producer responsibility regulations expand globally.
Innovation Ecosystems and Technological Advancement
The circular economy paper packaging sector benefits from robust innovation ecosystems that continuously expand application possibilities and performance boundaries. Research institutions collaborate with industry partners to develop next-generation materials that combine functionality with environmental responsibility.
Molded fiber technology represents one significant advancement, enabling the creation of complex three-dimensional forms from recycled paper pulp. These applications replace polystyrene and other problematic materials in electronics packaging, food service containers, and protective packaging systems while maintaining full compostability.
Nanotechnology applications enhance barrier properties through microscopic coatings that provide moisture and oxygen protection without compromising recyclability. These innovations expand paper packaging applications into previously plastic-dominated sectors including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and specialty foods.
Digital integration creates opportunities for smart circular economy paper packaging systems that optimize material usage through data-driven design and supply chain integration. Internet-of-Things sensors embedded in packaging provide real-time performance feedback that informs continuous improvement cycles and predictive maintenance schedules.
Supply Chain Transformation and Infrastructure Development
Successful circular economy paper packaging implementation requires coordinated supply chain transformation that aligns material flows with circular principles. This involves developing reverse logistics systems for packaging collection, establishing regional processing facilities for material recovery, and creating quality standards that ensure recycled content meets performance requirements.
Infrastructure investments in recycling technology and capacity expansion support increasing circular material flows. Advanced sorting systems utilizing artificial intelligence and optical recognition improve fiber recovery rates while reducing contamination levels that compromise recycled material quality.
Partnerships between packaging manufacturers, brand owners, retailers, and waste management companies create integrated systems where packaging materials flow seamlessly through multiple use cycles. These collaborations establish consistent quality standards, optimize transportation efficiency, and share costs across value chain participants.
Consumer Engagement and Behavioral Integration
The success of circular economy paper packaging depends significantly on consumer understanding and participation in circular systems. Education initiatives that communicate proper disposal methods, recycling protocols, and reuse opportunities maximize material recovery rates and system effectiveness.
Packaging design plays a crucial role in facilitating consumer engagement through clear labeling, intuitive functionality, and attractive aesthetics that encourage proper handling. Minimalist designs reduce material usage while sophisticated printing techniques maintain brand differentiation and shelf appeal.
Convenience factors influence consumer behavior substantially, requiring circular systems to match or exceed the ease of traditional linear packaging approaches. Innovations in packaging design prioritize user experience through features like easy-open mechanisms, resealable closures, and compact storage configurations.
Economic Models and Value Creation
Circular economy paper packaging creates value through multiple revenue streams and cost optimization opportunities. Traditional packaging represents a cost center for most companies, but circular approaches transform packaging into a value-generating asset through material recovery, brand differentiation, and customer engagement benefits.
Subscription and refill business models leverage durable paper packaging systems to reduce per-use packaging costs while enhancing customer lifetime value. These approaches particularly benefit direct-to-consumer brands seeking to build recurring revenue streams while demonstrating environmental commitment.
Industrial symbiosis opportunities enable paper packaging manufacturers to utilize waste streams from other industries as input materials, reducing raw material costs while providing waste management solutions for partner organizations. These collaborative approaches strengthen regional economic networks while advancing circular principles.
Regional Market Leadership and Global Expansion
Different global regions demonstrate varying levels of circular economy paper packaging adoption based on regulatory environments, consumer preferences, and infrastructure capabilities. Europe leads in regulatory framework development and consumer acceptance, while Asia-Pacific regions show rapid growth in manufacturing capacity and innovation investment.
North American markets benefit from established recycling infrastructure and strong consumer environmental awareness, creating favorable conditions for circular economy paper packaging expansion. Latin American regions present significant growth opportunities as environmental consciousness increases and regulatory frameworks develop.
Market leaders recognize that early investment in circular economy paper packaging capabilities creates competitive advantages that become more pronounced as regulations tighten and consumer preferences evolve. Companies establishing circular systems now position themselves favorably for long-term market leadership.
Future Outlook and Strategic Implications
The trajectory toward widespread circular economy paper packaging adoption appears irreversible as regulatory, economic, and social pressures align in favor of sustainable solutions. Organizations that proactively develop circular capabilities will capture increasing market share while those maintaining linear approaches face growing disadvantages.
Technology advancement continues accelerating, promising further improvements in paper packaging performance, cost-effectiveness, and application range. Investment in research and development, infrastructure, and partnership development provides the foundation for successful circular economy participation.
The integration of digital technologies, advanced materials science, and systems thinking creates unprecedented opportunities for innovation in circular economy paper packaging. Organizations that embrace these possibilities while maintaining focus on core circular principles will drive the next phase of sustainable packaging evolution.
The future of paper packaging in a circular economy represents both challenge and opportunity for businesses committed to environmental stewardship and long-term value creation. Success requires strategic vision, operational excellence, and collaborative engagement across extended value networks, but the rewards include enhanced competitiveness, improved customer relationships, and meaningful contribution to global sustainability objectives.





























