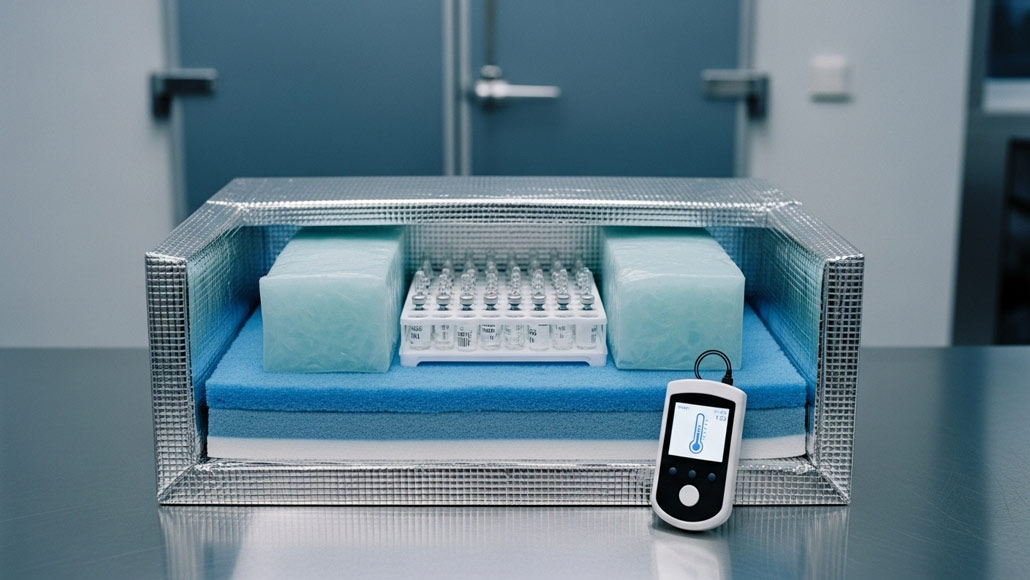
In the pharmaceutical logistics sector, maintaining precise temperature control is not just a compliance issue; it’s a critical necessity. Every year, the stakes rise as new therapies, intricate biologics, and fast-tracked vaccines demand ever tighter controls on thermal variance from warehouse to patient. While traditional insulated packaging has served the industry well, the march of innovation continues: today, advanced insulation materials are redefining the performance of pharma cold packs, helping global logistics providers and shippers ensure the integrity of life-saving medicines no matter the journey.
Recent advances have repositioned thermal protection not only as a safety imperative but also as a lever for cost efficiency, sustainability, and regulatory assurance. At the heart of this transformation are three principal material technologies: aerogels, vacuum insulation panels, and lightweight next-generation foams. Each demonstrates remarkable thermal performance and system flexibility, and all are accelerating the transition towards a more reliable and greener cold chain.
Rethinking Insulation for Cold Chain Demands
Advanced insulation materials have been propelled to prominence in part by surges in demand for high-value therapies and the globalization of pharmaceutical supply lines. As the industry shifts from local distribution to complex, intercontinental networks, the risks associated with temperature excursions multiply. This intensifies the search for materials that can consistently perform across varying climate extremes.
Traditional cold pack insulators, often employing expanded polystyrene or polyurethane foams, have inherent limitations, especially in demanding situations where space, weight, and duration pressure legacy materials to their thresholds. In response, R&D teams worldwide are advancing solutions that minimize thermal conductivity and maximize payload-to-mass ratios, ultimately enhancing both shipping efficiency and product safety.
Central to this progression is the rapid adoption of aerogel blankets and vacuum insulation panel (VIP) technology. Both materials have demonstrated exceptional ability to slow heat transfer, allowing cold packs to maintain critical temperatures for extended periods even when external conditions fluctuate. These solutions can translate to longer transit windows, greater route flexibility, and reduced refrigerant loads, all highly prized by pharma logistics planners.
Aerogels: The Promise of Nanoporous Performance
Among advanced insulation materials, aerogels occupy a unique position. Originally developed for aerospace and cryogenic applications, aerogels are highly porous solids composed almost entirely of air, conferring unrivaled thermal resistance per unit weight. Their structure, a matrix of silica or polymer-based strands interlaced with tiny, nanoscale pores, traps air and inhibits convection, dramatically limiting heat transfer.
Researchers have demonstrated that the incorporation of aerogel blankets into pharmaceutical cold pack designs can significantly reduce temperature gradients, supporting the stability of even highly sensitive bioproducts during transit. The near-weightlessness of aerogel further benefits cold chain logistics by minimizing shipping mass, a factor with concrete ramifications for air freight cost and carbon footprint alike.
Recent studies highlight that fiber-reinforced aerogel blankets (sometimes abbreviated as FRABs) deliver robust mechanical properties without sacrificing insulation efficiency. When tested against conventional perlite-based or bulk-fill systems, aerogel blankets maintained equivalent or superior insulation with less material thickness and a lower tendency to settle or degrade over repetitive cycles. This makes them especially appealing for reusable package solutions demanding both durability and high thermal performance.
While challenges remain, notably, the material’s inherent fragility and the premium price of production, the pharma logistics sector continues to integrate aerogels into its elite cold-pack systems, especially for long-haul or route-agnostic shipments where failure is not an option.
Vacuum Insulation Panels: Density With Discipline
Another leap forward in advanced insulation materials is marked by the entrance of vacuum insulation panels (VIPs) into the pharmaceutical sector. VIPs are composed of a rigid, porous core, often made of silica or polyurethane, enclosed in a gas-tight laminate and evacuated to create a vacuum barrier. This vacuum prevents most heat transfer by conduction and convection, enabling VIP-equipped packaging to deliver 5–10 times greater thermal resistance than comparably sized foam systems.
Pharmaceutical cold packs integrating VIPs exhibit extended hold times for critical temperature ranges, often allowing shipments to safely traverse continents with reduced ice pack or coolant requirements. VIPs have found particular value in supporting temperature-sensitive biologics and vaccines that are rendered ineffective by even minor deviations.
From a business perspective, VIPs drive value in two critical dimensions: they shrink the volume of non-revenue-generating “deadweight” in a shipping container, and, by holding temperature longer, they shrink the risk window for rejected deliveries or spoilage claims. Moreover, the passive nature of VIP technology, requiring no external power, aligns with industry sustainability goals, reducing the total environmental burden versus active cooling alternatives.
Still, VIPs are engineered solutions, requiring precise handling due to their rigid shapes and susceptibility to puncture. Recent innovations in encapsulation and edge-seal packages seek to address these mechanical vulnerabilities while retaining the material’s standout thermal properties. This seeks to expand VIP adoption in global pharma logistics.
Lightweight Insulation: Composites and Sustainable Cores
Lightweight insulation foams and novel composites have also established their place in the modern pharmaceutical cold chain by combining favorable weight profiles, manufacturability, and cost-effectiveness. New polyurethane, polyisocyanurate, and expanded polystyrene foams are infused with micro- or nano-particles that improve thermal stability, decrease density, and support environmental objectives through increased recyclability or compostability.
Deployment of lightweight composite panels is on the rise, particularly for single-use or mid-range cold packs that must hit rigorous performance thresholds while keeping system costs in check. When compared with legacy insulators, these next-generation foams consistently demonstrate a superior ratio of insulation value to weight, often outperforming traditional materials in head-to-head thermal decay trials.
A significant advantage of these advanced insulation materials, especially when engineered for modular package designs, is their flexibility in manufacturing, permitting custom sizing and integration with built-in humidity or shock controls, thus enhancing protection for complex drug formulations. These traits enable pharmaceutical distributors to optimize hardware for route-specific or payload-specific missions, bringing new levels of precision to the cold chain.
Integrating Advanced Materials Into Pharma Cold Chain Logistics
The successful deployment of advanced insulation materials is more than a technical challenge; it is a systems integration endeavor. Regulatory requirements such as those set by the World Health Organization and government health authorities mandate extensive validation, traceability, and temperature data logging for pharmaceuticals in transit. As a result, cold pack designers must harmonize cutting-edge insulation tech with sophisticated monitoring systems and efficient package geometries.
For industries where reliability is paramount and where a temperature excursion can mean the loss of an entire high-value shipment, the promise of advanced insulation materials is transformative. Integration with traditional insulating methods, the use of active monitoring devices, and the employment of phase-change materials (PCMs) within advanced insulation layers are helping supply chains adapt to increasingly stringent distribution requirements.
Moreover, the adoption of sustainable packaging mandates, now spreading through North America and the European Union, makes the environmental profile of insulation a new strategic lever for procurement teams. Materials that reduce total refrigerant requirements, allow for reduced shipping weight, and improve end-of-life recyclability contribute directly to the sector’s drive to achieve sustainability targets without compromising product quality.
The Road Ahead: Opportunities and Evolving Standards
As investments in global pharma logistics infrastructure continue, advanced insulation materials are set to become the backbone of next-generation cold chain solutions. Ongoing research is addressing challenges in mass-scale production, cost optimization, and the development of hybrid insulation packages that blend the best qualities of aerogels, VIPs, and cutting-edge foam composites.
Industry initiatives are underway to standardize testing protocols, benchmarking the real-world performance of insulation materials under simulated shipping conditions. These efforts aim to foster greater transparency, accelerate regulatory harmonization, and strengthen supply chain resilience.
With packaging design evolving in tandem with insulation advancements, the market is poised for ever-increasing integration across materials science, equipment validation, and sustainable logistics. Advanced insulation materials, once relegated to elite or experimental use cases, are now a mainstream part of the industry’s toolkit for balancing cost, performance, and compliance in the pharmaceutical cold chain.
Conclusion
Advanced insulation materials are reshaping the landscape of pharmaceutical cold chain logistics. Through the implementation of aerogels, vacuum insulation panels, and lightweight composite foams, shippers can achieve unparalleled levels of thermal control, enabling wider access to critical therapies worldwide.
These technological leaps have unlocked new efficiencies and supported critical compliance milestones, all while improving sustainability and reducing total logistics risk. As material science, regulations, and operational demands continue to evolve, further integration of advanced insulation solutions into pharmaceutical cold packs is inevitable, redefining best practices for a sector where precision and reliability make all the difference.





























