Reducing Packaging Waste: Paper Recycling and Reuse Models
The global imperative to reduce packaging waste has catalyzed innovative approaches that transform discarded materials from environmental liabilities into valuable resources through sophisticated recycling and reuse systems. Paper packaging recycling represents one of the most successful circular economy implementations, demonstrating how systematic waste reduction can create economic value while addressing environmental challenges.
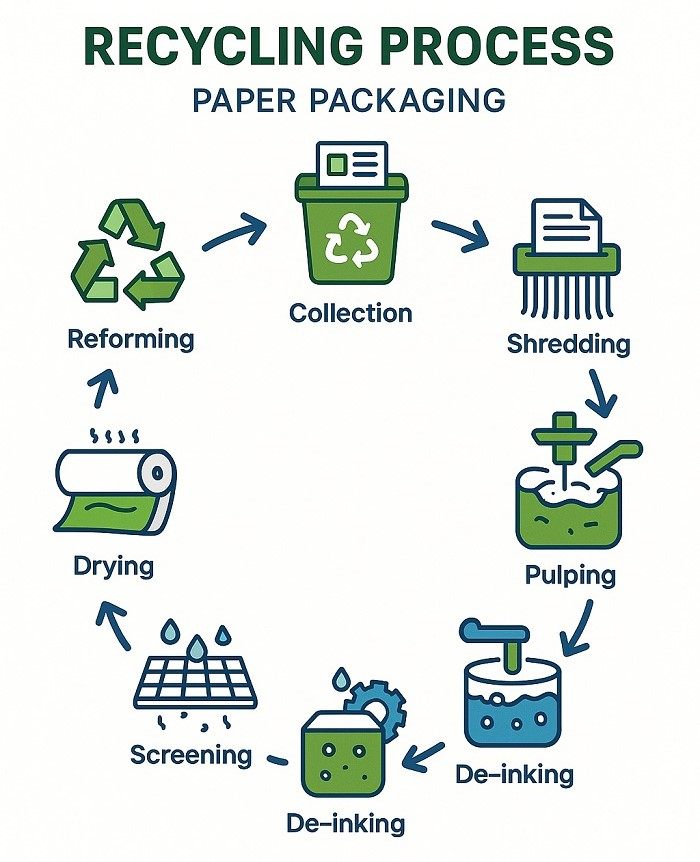
The Foundation of Paper Recycling Excellence
Paper packaging recycling achieves remarkable success rates that significantly exceed other packaging materials, with European facilities consistently achieving 87 percent recycling rates compared to 42 percent for plastic packaging. This superior performance reflects both the inherent properties of paper materials and the mature infrastructure systems developed to support circular material flows.
The recycling process for paper packaging begins with collection systems that separate materials at source or through advanced sorting facilities that utilize optical scanning, air classification, and density separation technologies. These sophisticated systems achieve high purity levels that ensure recycled fiber quality meets stringent manufacturing specifications for new packaging applications.
Advanced pulping technologies extract usable fibers from collected packaging materials while removing contaminants like adhesives, inks, and coatings that could compromise product quality. Modern de-inking processes utilize flotation, washing, and screening techniques that produce recycled pulp with brightness and strength characteristics suitable for high-quality packaging applications.
Quality control systems throughout recycling processes monitor fiber length, brightness levels, contamination rates, and strength properties to ensure recycled materials meet performance standards for specific end-use applications. This quality assurance enables recycled content to substitute for virgin materials without compromising packaging functionality or appearance.
Innovative Reuse Models Transforming Packaging Systems
Reuse models represent advanced approaches to packaging waste reduction that prevent materials from entering waste streams by extending useful life through multiple circulation cycles. These systems require coordinated infrastructure for collection, cleaning, inspection, and redistribution that creates new business opportunities while dramatically reducing environmental impact.
Return-based reuse systems enable packaging to be collected from consumers, professionally cleaned and refurbished, then redistributed for continued use. These models prove particularly effective for durable packaging applications like shipping containers, display cases, and protective packaging where structural integrity enables multiple use cycles.
Refill models allow consumers to reuse packaging containers through systems that provide product refills without requiring new primary packaging. These approaches reduce packaging material requirements by up to 90 percent while creating convenient, cost-effective solutions that appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Hybrid reuse systems combine elements of return and refill models to optimize convenience and environmental benefits across different application requirements. These flexible approaches accommodate varying product characteristics, consumer preferences, and logistical constraints while maximizing waste reduction benefits.
Industrial reuse applications focus on business-to-business packaging systems where higher volume flows and professional handling enable more sophisticated reuse approaches. Industrial users often achieve 20 or more reuse cycles for appropriate packaging designs, creating substantial cost savings while virtually eliminating packaging waste.

Technology Integration Enhancing Recycling Efficiency
Advanced technologies continue improving paper packaging recycling efficiency through automation, quality optimization, and contamination reduction that increase material recovery rates while reducing processing costs. Artificial intelligence applications optimize sorting processes by identifying different paper grades, contamination levels, and quality characteristics that enable precise material segregation.
Optical sorting systems utilizing hyperspectral imaging distinguish between different paper types, coating materials, and contamination levels with accuracy levels that exceed human sorting capabilities. These automated systems process materials continuously at high speeds while maintaining consistent quality standards that optimize recycled material value.
Chemical recycling innovations complement traditional mechanical recycling by breaking down paper fibers at molecular levels to remove contaminants that cannot be eliminated through conventional cleaning processes. These advanced techniques enable recycling of heavily printed or coated packaging materials that previously required disposal or energy recovery.
Digital tracking systems provide visibility throughout recycling processes, enabling optimization of collection routes, processing schedules, and material flows that reduce costs while improving service quality. Radio frequency identification tags and blockchain applications create transparent records of material sources, processing steps, and quality characteristics that support premium pricing for high-quality recycled materials.
Economic Models Supporting Sustainable Waste Reduction
The economics of paper packaging recycling have evolved to support profitable operations that create value for multiple stakeholders while achieving environmental objectives. Market demand for recycled content continues growing as brands seek to demonstrate environmental responsibility while meeting regulatory requirements for sustainable packaging.
Premium pricing for high-quality recycled materials reflects growing recognition that recycled content provides marketing value and regulatory compliance benefits that justify cost premiums over virgin materials. These price differentials create economic incentives for investment in advanced recycling technologies and quality improvement initiatives.
Extended producer responsibility programs increasingly require packaging manufacturers and brand owners to accept financial responsibility for end-of-life packaging management. These regulatory frameworks create direct economic incentives for designing recyclable packaging and supporting recycling infrastructure development.
Carbon credit markets provide additional revenue streams for packaging waste reduction initiatives by monetizing greenhouse gas emission reductions achieved through recycling and reuse programs. These environmental markets create financial value for waste reduction activities while supporting broader climate change mitigation objectives.
Supply Chain Integration and Logistics Optimization
Successful paper packaging recycling requires coordinated supply chains that efficiently collect, process, and redistribute materials while maintaining quality standards and minimizing transportation costs. Regional processing facilities located near major consumption centers reduce transportation requirements while providing convenient collection services for businesses and consumers.
Reverse logistics systems designed specifically for packaging waste management optimize collection routes, processing schedules, and redistribution networks to minimize costs while maximizing material recovery rates. These specialized logistics operations require different capabilities than traditional forward supply chains but create opportunities for service differentiation and customer value creation.
Integration with existing waste management infrastructure leverages established collection networks while adding specialized processing capabilities for paper packaging materials. This integration approach reduces infrastructure investment requirements while improving service coverage and operational efficiency.
Collaborative networks among packaging manufacturers, brand owners, retailers, and recycling processors create shared value through coordinated waste reduction efforts. These partnerships distribute costs and benefits across multiple stakeholders while achieving economies of scale that improve overall system efficiency.
Regulatory Frameworks Supporting Circular Systems
Government regulations increasingly support paper packaging recycling through mandates, incentives, and infrastructure investments that create favorable operating environments for circular business models. Packaging waste regulations in major markets require minimum recycled content levels, recyclability standards, and waste reduction targets that drive demand for recycling services.
Tax incentives and subsidies for recycling operations reduce capital requirements and operating costs while providing competitive advantages over disposal-based waste management approaches. These financial incentives accelerate adoption of advanced recycling technologies while supporting infrastructure development in underserved regions.
Standards and certification programs provide quality assurance for recycled materials while creating market recognition for recycling achievements. These programs reduce transaction costs by providing common quality metrics while supporting premium pricing for certified recycled materials.
Public procurement policies that prioritize recycled content create stable demand for recycled packaging materials while demonstrating government commitment to circular economy principles. These policies provide predictable revenue streams that support long-term investment in recycling infrastructure and technology development.
Consumer Engagement and Behavioral Change
Successful paper packaging recycling depends significantly on consumer participation in collection systems and proper waste separation practices. Educational initiatives that communicate recycling procedures, contamination prevention, and environmental benefits increase participation rates while improving material quality.
Convenience factors strongly influence consumer recycling behavior, requiring systems that minimize effort and complexity while providing clear guidance about proper procedures. Standardized labeling, accessible collection points, and simplified sorting requirements increase participation rates across diverse demographic groups.
Incentive programs that provide direct benefits to consumers for recycling participation create measurable behavior change while generating positive associations with recycling activities. These programs range from monetary rewards to social recognition systems that appeal to different motivational factors.
Feedback mechanisms that communicate recycling results and environmental impact create awareness about individual contributions to waste reduction while encouraging continued participation. Digital platforms enable personalized feedback that maintains engagement while providing education about recycling benefits and procedures.
Innovation in Recycling Technologies and Processes
Continuous innovation in paper packaging recycling addresses technical challenges while improving efficiency and expanding material recovery possibilities. Advanced fiber recovery techniques extract usable materials from increasingly complex packaging designs that incorporate multiple materials and sophisticated coating systems.
Biotechnology applications utilize enzyme systems and microbial processes to break down adhesives and coatings that interfere with traditional recycling processes. These biological approaches offer environmentally friendly alternatives to chemical processing while achieving high separation efficiency for complex packaging materials.
Membrane separation technologies provide precise control over material purification processes, enabling recovery of high-quality fibers from heavily contaminated waste streams. These advanced separation techniques expand recycling possibilities for packaging materials that previously required disposal due to contamination levels.
Closed-loop recycling systems that integrate collection, processing, and remanufacturing within single facilities optimize material quality while minimizing transportation and handling costs. These integrated approaches achieve higher recovery rates while reducing contamination risks throughout processing cycles.
Future Trends and Strategic Implications
The evolution of paper packaging recycling continues accelerating as technological advances, regulatory requirements, and market demand converge to create increasingly sophisticated waste reduction systems. Emerging trends include expanded automation, enhanced quality control, and integration with digital platforms that optimize operations while improving customer service.
Artificial intelligence applications will optimize recycling operations through predictive maintenance, quality monitoring, and process optimization that improve efficiency while reducing costs. Machine learning algorithms will identify optimal processing parameters for different material types while minimizing energy consumption and waste generation.
Blockchain technology will provide transparent tracking of recycled materials throughout supply chains, enabling verification of recycled content claims while supporting premium pricing for certified materials. This transparency will reduce fraud while increasing consumer confidence in recycling system effectiveness.
The integration of recycling operations with manufacturing processes will create seamless circular systems where waste materials flow directly into new product production without intermediate storage or transportation requirements. These integrated approaches will achieve higher efficiency while reducing costs and environmental impact.
Organizations that invest proactively in advanced recycling capabilities while building collaborative partnerships across extended supply chains will establish competitive advantages that strengthen as regulatory requirements increase and consumer demand for sustainable packaging continues growing.





























